Right now, you are reading words. If you continue to read these words, you will learn a lot more about grammar. Specifically, we are going to learn about a neat way to use verbs. I am talking about the way that we use verbs to describe actions that are happening right now. So, let’s not waste any more time and check out a cool part of grammar known as the present continuous tense.
What is present continuous tense?
We use verbs to refer to actions and states. To do so, we use many different types of verb tenses to say when actions occur or when states exist. The tense of a verb indicates when in time an event happened. Right now, we are going to look at a particular verb tense that refers to something that happens in the present but also keeps the fun going in the future: the present continuous tense. The present continuous tense, also called the present progressive tense, is a versatile verb tense that can refer to actions that are happening currently in the present and/or that happen in the future.
For example, the sentence I am washing my car expresses the thought that I am washing my car right now and I will continue to do so for some time in the future. The present continuous tense refers to actions and states that happen in the present but are continuous, that is, they still are ongoing and haven’t ended yet—that we know of right now, at least. I am obviously not going to wash my car forever!
When do you use present continuous?
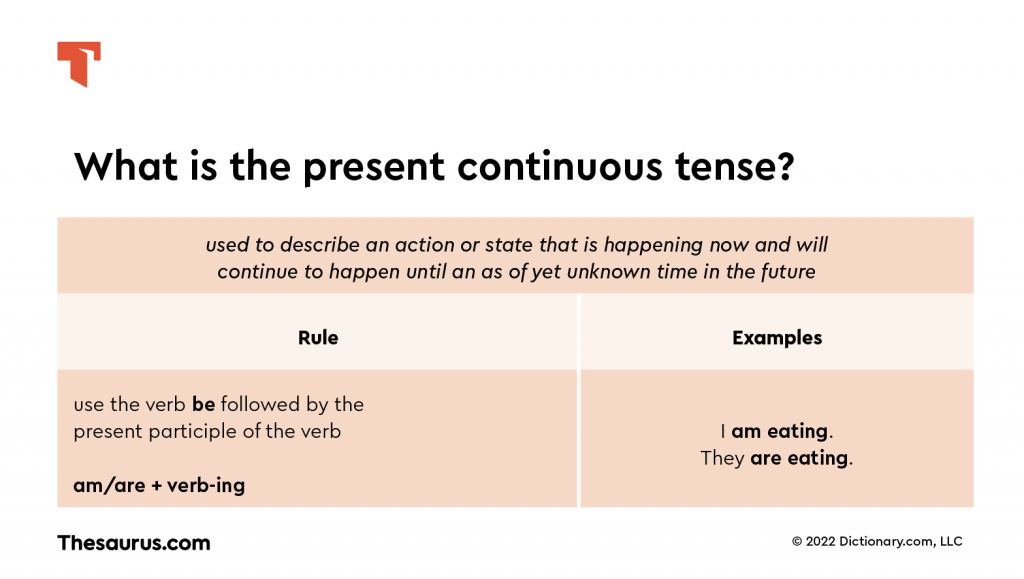
We often use the present continuous tense to refer to temporary states or actions. Putting it another way, we use the present continuous tense to describe an action or state that is happening now and will continue to happen until an as of yet unknown time in the future. Here are two examples of sentences that use the present continuous tense this way:
- Meghan is reading a book in the living room.
- My cat is watching the birds through the window.
Both of these sentences refer to actions that are being done for the moment but will stop when Meghan or that hungry cat does something else. We use the present continuous tense to indicate such a continuous action or state.
Because English grammar loves to make things difficult for us, we also often use the present continuous tense to refer to future events, especially ones that have been planned. When we do this, we often use adverbs of time to clarify that the present continuous tense is being used to refer to a future event rather than an event already in progress.
- I am going to Portugal this summer.
- We are celebrating Ben’s birthday next week.
There is one important caveat to keep in mind when using the present continuous tense. Typically, we don’t use the present continuous tense with stative verbs. Generally speaking, stative verbs describe states of existence rather than actions, so it usually doesn’t make sense to refer to them as being “in progress.” The following two sentences show incorrect use of the present continuous tense with stative verbs. You will probably notice how odd these sentences sound.
- That watch is looking cheap.
- My daughter is believing in Santa Claus.
Instead, we would use the simple present tense:
- That watch looks cheap.
- My daughter believes in Santa Claus.
Be careful of verbs that could be used as either stative or nonstative verbs depending on meaning or context.
For instance, we more commonly say Amanda appears sad today rather than Amanda is appearing sad today. On the other hand, we usually say The defendant is appearing in court tonight for such an upcoming event, rather than The defendant appears in court tonight.
How to form present continuous tense
To form the present continuous tense, we use the verb be followed by the present participle of the verb. The present participle is a form of a verb that ends in the suffix -ing. For example, the present participle of eat is eating. When using the present continuous tense, the verb be must be correctly conjugated so it agrees with the subject. For example:
- I am eating
- You are eating
- He/she/it is eating
- We are eating
- You are eating
- They are eating
Here are examples of the present continuous tense used in several sentences. Notice that the verb be is correctly conjugated to agree with the subject.
- I am studying for my algebra test.
- My lazy dog is snoring loudly.
- We are going to the beach during summer vacation.
How to make present continuous tense negative
In order to make the present continuous tense negative, all you need to do is put the word not between the verb be and the present participle. Contractions are also fine.
- I am not listening to his dumb jokes.
- She isn’t enjoying her time at the amusement park because of her toothache.
- Luckily, those hungry wolves aren’t heading this way.
No time like the present to improve your grammar!
You won’t mistake your verb tenses again when you check your writing on Thesaurus.com’s Grammar Coach™. This writing tool uses machine learning technology uniquely designed to catch grammar and spelling errors. Its Synonym Swap will find the best nouns, adjectives, and more to help say what you really mean, guiding you toward clearer, stronger, writing.
Whether you’re writing about the past, present, or future, start writing smarter today!